Definition
SPACE
Radiation invisible to human eyes
This means that when humans send a satellite to a distant planet, the object will not encounter "drag" in the same way that an airplane does as it sails through space.
Black holes
Smaller black holes can form from the gravitational collapse of a gigantic star, which forms a singularity from which nothing can escape — not even light, hence the name of the object.
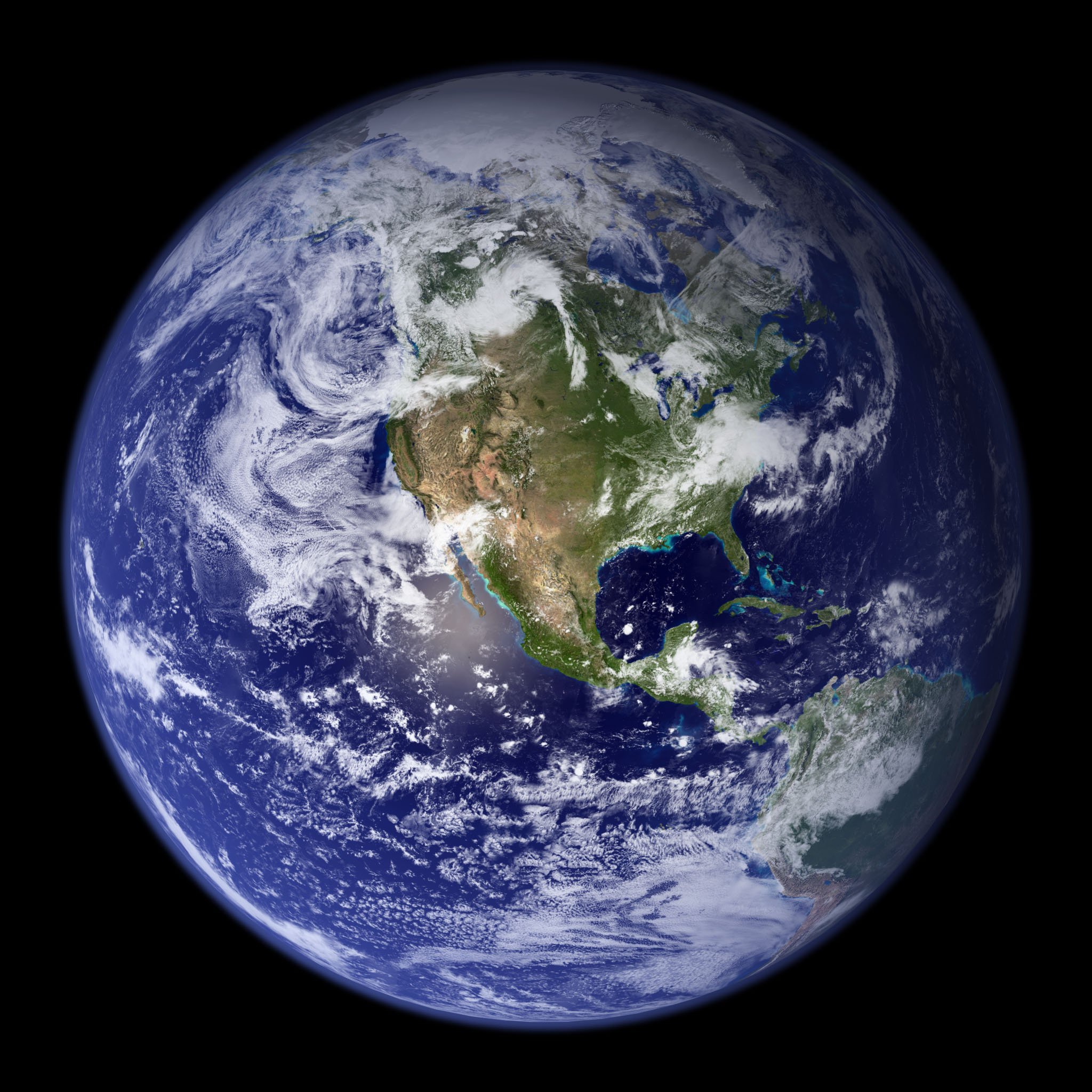
Stars, planets, asteroids and comets
Stars, planets, asteroids and comets are the building blocks of the solar system. Apart from that, there are also suns, meteoroids and satellites.
Galaxies and quasars
There are several types of galaxies, ranging from spiral to elliptical to irregular, and they can change as they come close to other objects or as stars within them age.